SQL Joins
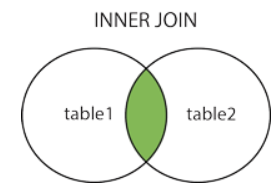
Joins are used to combine rows from two or more tables based on related columns between them. Joins allow you to retrieve data from multiple tables simultaneously, enabling you to create complex queries that fetch data from different sources. There are different types of joins in SQL, including: INNER JOIN Returns only the rows that have matching values in both tables based on the specified join condition. It discards non-matching rows from both tables. Example: create table t1(x int); insert into t1 values(1); insert into t1 values(1); insert into t1 values(0); create table t2(y int); insert into t2 values(0); insert into t2 values(1); insert into t2 values(1); select * from t1 inner join t2 on t1.x = t2.y Output: 2. LEFT JOIN (or) LEFT OUTER JOIN Returns all the rows from the left (or first) table and the matching rows from the rig...